Contact Companies
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
Get Your Company Listed on this Power Page
Introduction
This article takes an in-depth look at RF shielding.
Read further and learn more about topics such as:
- What is RF shielding
- Nature of radio frequency interference
- RF shielding materials
- Common forms of RF shielding
- And much more…

Chapter 1: What is RF Shielding?
Radiofrequency (RF) shielding involves blocking radiofrequency electromagnetic signals to prevent radio frequency interference (RFI), which can disrupt the normal operation of electronic devices. This is achieved by installing barriers made from conductive and magnetic materials around electronic circuits, cable lines, and both sources and targets of electromagnetic fields to isolate them from their surroundings. The effectiveness of RF shielding in minimizing interference depends on various factors, including the properties of the shielding material, the design, the thickness of the shield, the frequency of the electromagnetic signals, and the presence of any discontinuities in the shield.
Radiofrequency interference (RFI) can significantly impact the performance of electronic and communication devices, with each device responding differently to RFI. This interference can lead to system malfunctions, data loss, security breaches, and even device failure. While RFI is prevalent in modern electronics and cannot be completely eradicated, RF shielding is an effective measure to protect devices and equipment from the adverse effects of RF interference.
Chapter 2: What is the nature of radio frequency interference?
Electromagnetic waves transport energy and comprise an electric and a magnetic wave oscillating perpendicular to each other. These waves are defined by their wavelength and frequency, and their range is represented in the electromagnetic spectrum.

Electromagnetic Interference and Radio Frequency Interference
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) happens when unwanted electromagnetic signals disrupt the normal operation of electrical devices. This type of disturbance is often called "electromagnetic noise" or just "noise." But what sets EMI apart from radiofrequency interference (RFI)?
Interference can be caused by electromagnetic radiation at any frequency. Radiofrequency interference (RFI) is a specific type of EMI that occurs when the interfering electromagnetic waves fall within the radio frequency range of the electromagnetic spectrum, which spans from 3 kilohertz to 300 gigahertz. While EMI is the broader term, RFI is a subset of EMI that specifically refers to interference within the radio frequency portion of the spectrum.

Types of Radio Frequency Interference
Radiofrequency interference can be categorized based on its source, duration, and bandwidth.
Source
Natural Sources
Naturally occurring RFI is produced by astronomical events such as lightning strikes, solar flares, cosmic noise, static electricity, and environmental conditions like dust and snowstorms.
Man-Made Sources
Electronic and electrical devices can emit electromagnetic radiation that may interfere with other nearby devices and equipment. Man-made sources of RFI are classified into two categories: unintentional and intentional sources:
-
Unintentional Sources Equipment such as electric motors and generators, lightings, rectifiers, inverters, satellites, and transmission lines disrupt other nearby devices as a result of switching large electrical currents. However, the emission of electromagnetic radiation is purely incidental.
Electronic devices operating using wireless signals such as cellphones, laptops, Bluetooth mice and speakers, wireless routers, and remote controls are abundant sources of RFI. As these devices become faster, the frequency increases and more electromagnetic radiation is emitted in the surroundings. The electromagnetic radiation that leaks out from these devices would cause interference.
- Intentional Sources Intentional RFI sources are devices designed to emit electromagnetic energy. These sources include radars, jamming devices, and radio transmitters.

Duration
Continuous radiofrequency interference involves RFIs that are emitted steadily by a source through conduction or radiation. In contrast, impulse radio frequency interference appears sporadically or for brief periods. This type of interference is often caused by devices such as switches and lighting, which disrupt the voltage and current balance of nearby equipment. Both natural and man-made sources can produce these types of RFI.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the frequency range over which RFI is experienced.
Narrowband
Narrowband RFI consists of a single frequency or a narrow band of frequencies. It may result from oscillators or from spurious signals caused by various distortions in transmitters. Although narrowband RFI typically has a limited impact on electronic devices, it must be controlled to avoid interference. Devices such as mobile phones and Wi-Fi routers can emit narrowband RFI.
Broadband
Broadband RFI spans a wide range of frequencies across a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. This type of interference is not confined to a single signal. Broadband RFI can be caused by both natural and artificial sources. For example, the sun can obscure desired satellite signals used in communication systems, while other sources include arc welding, faulty power lines, and malfunctioning motor brushes.
Coupling Mechanisms
The coupling mechanism describes how electromagnetic waves or signals from a source reach the receiver or affected device, leading to RFI. The primary coupling mechanisms are as follows:

Radiation Coupling
Radiation coupling is the most commonly observed RFI coupling mechanism. In this method, electromagnetic waves travel through the air from the source to the receiver without requiring physical contact. The source and receiver can be separated by a significant distance.
Conduction Coupling
Conduction coupling happens when RFI travels along conductors such as wires and cables that connect the source to the receiver. This type of coupling is frequently seen in power supply lines and relies on the magnetic component of the electromagnetic wave. Installing shields around electrical wiring can help mitigate this type of interference.
Capacitive Coupling
Capacitive coupling occurs when electrical charge from a source is transferred to a receiving circuit due to charge differences. This happens between circuits that are very close to each other, usually less than a wavelength apart.
Magnetic Coupling
Magnetic coupling, or induction coupling, takes place when a varying magnetic field exists between the source and the receiver's conductor loops. This process transfers RFI to the receiver through electromagnetic induction, typically occurring between closely spaced conductors.
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers
Chapter 3: What are RF shielding materials?
The effectiveness of shielding is influenced by the material's electrical conductivity, magnetic permeability, the frequency of the electromagnetic wave, and the shield's geometry. High electrical conductivity allows the material to block or reflect the electric component of electromagnetic waves effectively. Conversely, high magnetic permeability provides a low reluctance path for magnetic flux, which helps in absorbing and redirecting magnetic fluxes around the shielded area. The choice of materials is determined by the relative strengths of the electric and magnetic components of the electromagnetic field.
Common RF shielding materials include the following:
Copper
Copper is a highly effective RF shielding material due to its excellent ability to absorb and attenuate both electric and magnetic components of electromagnetic waves. It boasts high electrical conductivity.
Copper is also easy to fabricate into various shapes, allowing copper-based shields to be installed on electronic devices with relative ease. Additionally, copper is naturally resistant to corrosion and can withstand oxidation from environmental factors.
Copper alloys such as phosphorus bronze, beryllium copper, brass, and bronze are used as RF shielding material. The elasticity of phosphorus bronze and beryllium copper makes them useful in contact applications for batteries and springs. However, despite its excellent RF shielding properties, copper costs more compared to other materials.

Nickel Silver (Copper Alloy 770)
Nickel silver, also known as copper alloy 770, is composed of varying amounts of nickel, copper, and zinc. It is frequently used for RF shielding in highly corrosive environments. It effectively attenuates RFI across frequencies from mid-kHz to GHz. With a permeability of 1, nickel silver is particularly suitable for constructing RF shields for MRI machines, where magnetic interference must be minimized.
Nickel silver is naturally corrosion-resistant and solderable without the need for additional plating. It also has a visually appealing bright silver finish, despite not containing actual silver.

Aluminum
Aluminum is a non-ferrous metal known for its high electrical conductivity and favorable strength-to-weight ratio, making it a versatile material. Thin aluminum sheets are effective at blocking low-frequency radio waves. It is often used to construct enclosures for electronic devices to provide built-in RF protection. Although aluminum has 50-60% of the conductivity of copper, it requires greater thickness to achieve the same level of shielding effectiveness as copper. Aluminum is susceptible to galvanic corrosion and oxidation, forming oxides on its surface when exposed to the environment. Additionally, it has poor solderability on its own.

Steel
Steels come in various forms and with different alloy contents. Ferromagnetic materials like steels provide effective shielding against low-frequency magnetic fields, which copper alloys and aluminum do not offer. The RF shielding and mechanical properties of steels vary based on their specific type.
Low carbon steels offer higher permeability and saturation points compared to high carbon steels. These properties are crucial for effectively drawing the magnetic component of electromagnetic waves in RF shielding. The saturation point indicates the maximum magnetic flux density that a material can support at a particular thickness.
Annealed steels have enhanced magnetic properties. Annealing enlarges the grain structure and relieves the internal stress of steel. The grain orientation of steels must be in the same direction as the magnetic flux to provide a low reluctance path. Lastly, cold-rolled steels possess better magnetic shielding properties, but hot-rolled steels have better mechanical properties.
Mu-Metal
Mu-metal is a soft ferromagnetic alloy composed of about 80-82% nickel, 5% molybdenum, with alloying elements like copper and silicon, and iron as the balance. It boasts exceptional magnetic permeability and offers excellent ductility and malleability, making it easy to shape into various forms. Mu-metal is used in RF shielding for electric power transformers, MRI equipment, hard disks, sensors, and other delicate electronic devices.

Pre-Tin Plated Steel
Pre-tin plated steel is a cost-effective material used for RF shielding, particularly effective across the kHz to lower GHz frequency ranges. The tin coating not only protects against corrosion but also facilitates soldering during assembly processes.
Various coating methods such as plating, flame spraying, metallization, and sputtering are employed to enhance the durability, solderability, and surface compatibility of metals. Commonly used coatings include tin, tin-lead, zinc, gold, and chromium compounds.
Conductive Elastomers
Due to its flexibility, elastomeric materials can be easily processed into different forms of RF shielding, such as gaskets, O-rings, and linings. They are made electrically conductive to block electromagnetic waves by coating and loading them with metal fillers such as nickel graphite, silver copper, and silver aluminum. These materials provide a conductive path along shielding seams and other openings in electronic closures to block electromagnetic fields from the environment completely. Elastomer-based RF shielding with adhesive backing is available for easy installation.
The common elastomeric materials used in RF shielding are silicone rubber, fluorosilicone rubber, EPDM, and neoprene. These materials are highly flexible synthetic elastomers. They have good resistance to UV rays, ozone, oxidation, weathering, and many chemical substances. They possess high thermal and dimensional stability and are ideal for outdoor and harsh environments.

Conductive Fabrics
Conductive fabrics are textiles that have been treated or blended with metals like nickel, copper, silver, gold, or carbon. These fabrics offer effective shielding against RFI and are commonly used to reduce electromagnetic interference in confined areas. The fibers used to create these fabrics include polyester, cotton, silk, and nylon.

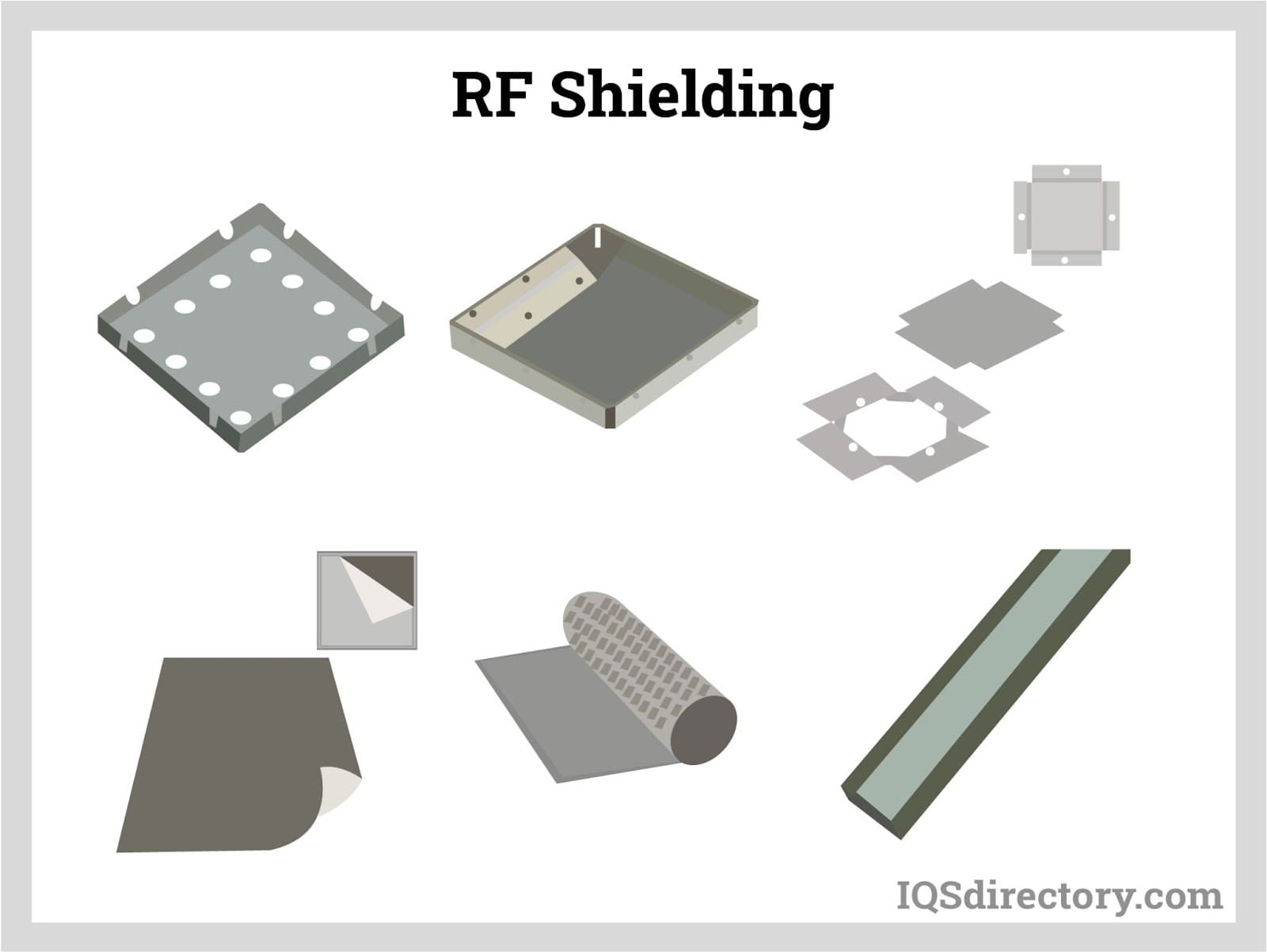
Chapter 4: What are the common forms of RF shielding?
Here are some common types and forms of RF shielding, along with their operational principles and design factors:
Wire Mesh and Screens as a Faraday Cage
A Faraday cage is a continuous and conductive enclosure made of wire mesh or screens that blocks static and non-static electromagnetic fields. It works by distributing the electromagnetic waves around the exterior of the cage. Without an electric field, the electric charges within the conductive cage are evenly distributed around the material. When an external electric field is applied to the cage, it will cause the charges to immediately redistribute and cause electron flow around the cage. Thus, a secondary electric field in the opposite direction is created. Both electric and incoming fields cancel each other; hence, the net electric field is zero.

A Faraday cage operates by absorbing and reducing magnetic fields through its design. The material's magnetic permeability helps reroute the flux lines of incoming magnetic fields. As the magnetic field interacts with the conductor, it induces eddy currents within the material. These eddy currents create a secondary magnetic field that counteracts the incoming field. Consequently, the magnetic field within the Faraday cage is minimized. This principle is foundational to the functioning of various other RF shielding types.

Faraday cages are very effective at attenuating low-frequency electromagnetic waves. However, they may not be as effective against high-frequency waves (such as those used in HF RFID), which can penetrate the shielding. To block these high-frequency waves effectively, the holes in the cage should be smaller than 1/10th of the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave.

Solid Enclosures
Solid enclosures are sturdy casings designed to prevent electromagnetic fields from entering or escaping. Constructed from continuous metal and featuring minimal openings, they have fewer gaps and can block a broader spectrum of electromagnetic waves compared to wire mesh or screens. However, these enclosures offer limited ventilation to the components inside. To prevent electric shock, solid enclosures are grounded to redirect any stray currents on their surface.

Gaskets and O-rings
Faraday cages and solid enclosures often feature openings like doors and lids for accessing the protected electronic components. These openings can disrupt the shielding effect and significantly reduce the overall effectiveness. To maintain proper shielding, it's advisable to use RF gaskets or O-rings to ensure a complete seal.
RF gaskets and O-rings are commonly made from elastomeric materials that are enhanced with metal fillers. Elastomers are favored for their flexibility and durability, while metal gaskets, though strong, may deform under sealing pressures. It's crucial to ensure that the gaskets and O-rings are compatible with the surfaces they are meant to seal.


Cable Shielding
A cable shielding is wrapped around and runs coaxially with the insulating layer of the power-carrying conductor. It is used in instrumental wiring to prevent external electromagnetic waves from interfering with the signals to be delivered to the instrument. It is also used in power cables to block electromagnetic waves from escaping and interfering with nearby electrical or electronic devices. Cable shielding is usually grounded. There are three types of cable shielding:
-
Foil shields block frequencies greater than 15 kHz. They can be made from materials such as aluminum, copper, conductive polymers, or metal-coated textiles. Since foils are thin materials, they might be damaged when excessively flexed or stretched and cause discontinuities.

-
Spiral shields consist of strands of copper wires spiraling around the insulator of the conductor. It is easy to install in cables and inexpensive. However, the winding can loosen and cause discontinuities if the cable is stretched, bent, or twisted.

- Braided shields are made of woven wires made from bare or tinned copper, nickel, or silver. They have high strength and flexibility. They can be easily terminated when crimping or soldering to a connector. However, they do not guarantee full shielding coverage, and small discontinuities may be present. Shielding coverage depends on the tightness of the woven wires. Braided shields are recommended for blocking low-frequency waves.

Shielded Vents
Shielded vents, also known as shielded honeycomb vent panels, are used to allow airflow and manage heat dissipation for cooling electronic components within solid enclosures. It is essential that these vents are specifically designed to meet the cooling needs of the device while preserving the enclosure's shielding effectiveness.

Board-Level Shielding
Board-level shielding prevents electromagnetic signals from entering or exiting the components at the board level. This shielding can come in either single-piece or multi-piece designs, typically consisting of a cage or solid enclosure along with various RF seals and fittings.

RF-Shielded Facilities
RF shielding is essential in various sectors, including IT, healthcare, military, banking, business, government, research, and testing facilities, to prevent external RF signals from interfering. RF enclosures help safeguard sensitive and confidential information, thwart espionage, cyberattacks, and data breaches, and ensure the accuracy and reliability of the electronic equipment’s results and operations within the facility.

An MRI room is a prime example of an RF-shielded environment. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines utilize powerful magnetic fields and radio waves for body imaging. External RF signals and magnetic fields can interfere with these machines, leading to distorted images. Additionally, MRI machines emit electromagnetic radiation that might affect other medical devices.
To maintain RF shielding, facilities employ conductive sheets made from materials like copper, aluminum, and steel, which cover walls, ceilings, doors, windows, floors, and partitions. Conductive fittings are used to seal seams effectively. Ensuring that all six surfaces of the room are covered is essential, as any gaps can compromise the shielding effectiveness.
Chapter 5: Who are the leading manufacturers of RFI shielding machines?
Numerous machines are available for RFI (Radio Frequency Interference) shielding, crucial in modern times for establishing electromagnetic barriers that prevent unwanted radio frequency signals from disrupting sensitive electronic devices. This ensures reliable operation and communication across various industries, including telecommunications, electronics, and wireless technologies. Below, we review several brands in the United States and Canada that manufacture RFI shielding materials, detailing their specific models, capabilities, features, and components:
Brand: Laird Performance Materials
Model: Shielding Material Production Equipment
Features: Laird Performance Materials provides machinery for creating RFI shielding materials, including conductive gaskets, absorbers, and ferrites. Their production systems feature specialized equipment for extrusion, molding, and die-cutting, allowing precise control over material characteristics, thickness, and design. The equipment supports the manufacturing of RFI shielding materials with outstanding electrical conductivity and shielding efficiency. Laird's production technology guarantees high-quality RFI shielding solutions suited for various applications.
Brand: Tech-Etch
Model: RFI Shielding Gasket Manufacturing Systems
Features: Tech-Etch is known for its advanced systems designed to manufacture RFI shielding gaskets.
These systems utilize machinery for stamping, etching, and plating processes. They provide precise control over the dimensions, materials, and finishes of gaskets, enabling high-volume production without compromising quality or consistency. Tech-Etch’s equipment is tailored to meet the specific needs of customers and adhere to industry standards.
Brand: Leader Tech Inc.
Model: RFI Shielding Material Manufacturing Equipment
Features: Leader Tech Inc. offers equipment for creating RFI shielding materials such as conductive elastomers, tapes, and thermal pads. Their machinery includes systems for mixing and dispensing, extruding, and curing. This equipment allows for precise control over the formulation, shaping, and curing processes of RFI shielding materials. It also supports customization in terms of material properties, shapes, and sizes. Leader Tech’s equipment ensures the production of high-quality, reliable RFI shielding materials.
Brand: Chomerics (a division of Parker Hannifin)
Model: RFI Shielding Material Production Equipment
Features: Chomerics provides equipment for the production of RFI shielding materials including conductive films, coatings, and gaskets. Their equipment comprises coating systems, curing ovens, and converting machinery, which offer precise control over material application, thickness, and curing processes. This machinery supports the creation of RFI shielding materials that exhibit high effectiveness and durability. Chomerics’ equipment is designed to ensure efficient and reliable manufacturing of RFI shielding products.
Brand: Henkel Electronic Materials (formerly The Bergquist Company)
Model: RFI Shielding Material Manufacturing Systems
Features: Henkel Electronic Materials provides manufacturing systems for creating RFI shielding materials, such as conductive thermal interface materials, adhesives, and films. Their systems feature coating and lamination machines, curing units, and converting equipment. These systems allow for accurate control over material application, curing, and conversion, supporting both large-scale production and tailored solutions for particular needs. Henkel Electronic Materials' equipment ensures high performance and dependable RFI shielding materials.
Please be aware that the availability and specifics of models may differ, so it is recommended to reach out to the manufacturers or their authorized distributors for the most current information on models that fit your needs.
Conclusion
- Radiofrequency (RF) shielding is the practice of blocking radiofrequency electromagnetic signals that cause radio frequency interference (RFI).
- RFI decreases the performance of electronic devices and can induce devastating effects.
- The use of RF shielding is a measure to safeguard our devices and equipment from the harmful effects brought by RFI. RF shielding is accomplished by installing barriers around potential sources and victims of electromagnetic fields.
- RF shielding materials must have high conductivity and magnetic permeability.
- The common metal RF shielding materials are copper, aluminum, nickel silver, pre-tin plated steel, and Mu-metal.
- Elastomers and textile fibers can also be used as an RF shielding material by making them conductive first by adding metal fillers and coating. The common elastomers are silicone rubber, fluorosilicone rubber, EPDM, and neoprene, while the common textile fibers are polyester, nylon, silk, and cotton.
- The common forms of RF shielding are wire mesh and screens, solid enclosures, gaskets and O-rings, cable shielding, shielded vents, board-level shielding, and RF-shielded facilities.


