Last Updated : 26 Jun, 2024
Comments
Improve
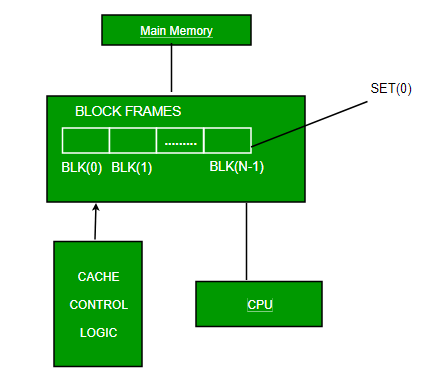
Cache memory is a small, high-speed storage area in a computer. The cache is a smaller and faster memory that stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. There are various independent caches in a CPU, which store instructions and data. The most important use of cache memory is that it is used to reduce the average time to access data from the main memory.
By storing this information closer to the CPU, cache memory helps speed up the overall processing time. Cache memory is much faster than the main memory (RAM). When the CPU needs data, it first checks the cache. If the data is there, the CPU can access it quickly. If not, it must fetch the data from the slower main memory.
Characteristics of Cache Memory
- Cache memory is an extremely fast memory type that acts as a buffer between RAM and the CPU.
- Cache Memory holds frequently requested data and instructions so that they are immediately available to the CPU when needed.
- Cache memory is costlier than main memory or disk memory but more economical than CPU registers.
- Cache Memory is used to speed up and synchronize with a high-speed CPU.

Cache Memory
Levels of Memory
- Level 1 or Register: It is a type of memory in which data is stored and accepted that are immediately stored in the CPU. The most commonly used register is Accumulator, Program counter, Address Register, etc.
- Level 2 or Cache memory: It is the fastest memory that has faster access time where data is temporarily stored for faster access.
- Level 3 or Main Memory: It is the memory on which the computer works currently. It is small in size and once power is off data no longer stays in this memory.
- Level 4 or Secondary Memory: It is external memory that is not as fast as the main memory but data stays permanently in this memory.
Cache Performance
When the processor needs to read or write a location in the main memory, it first checks for a corresponding entry in the cache.
- If the processor finds that the memory location is in the cache, a Cache Hit has occurred and data is read from the cache.
- If the processor does not find the memory location in the cache, a cache miss has occurred. For a cache miss, the cache allocates a new entry and copies in data from the main memory, then the request is fulfilled from the contents of the cache.
The performance of cache memory is frequently measured in terms of a quantity called Hit ratio.
Hit Ratio(H) = hit / (hit + miss) = no. of hits/total accesses
Miss Ratio = miss / (hit + miss) = no. of miss/total accesses = 1 - hit ratio(H)
We can improve Cache performance using higher cache block size, and higher associativity, reduce miss rate, reduce miss penalty, and reduce the time to hit in the cache.
Cache Mapping
There are three different types of mapping used for the purpose of cache memory which is as follows:
- Direct Mapping
- Associative Mapping
- Set-Associative Mapping
1. Direct Mapping
The simplest technique, known as direct mapping, maps each block of main memory into only one possible cache line. or In Direct mapping, assign each memory block to a specific line in the cache. If a line is previously taken up by a memory block when a new block needs to be loaded, the old block is trashed. An address space is split into two parts index field and a tag field. The cache is used to store the tag field whereas the rest is stored in the main memory. Direct mapping`s performance is directly proportional to the Hit ratio.
i = j modulo m
where
i = cache line number
j = main memory block number
m = number of lines in the cache

Direct Mapping
For purposes of cache access, each main memory address can be viewed as consisting of three fields. The least significant w bits identify a unique word or byte within a block of main memory. In most contemporary machines, the address is at the byte level. The remaining s bits specify one of the 2s blocks of main memory. The cache logic interprets these s bits as a tag of s-r bits (the most significant portion) and a line field of r bits. This latter field identifies one of the m=2r lines of the cache. Line offset is index bits in the direct mapping.

Direct Mapping – Structure
2. Associative Mapping
In this type of mapping, associative memory is used to store the content and addresses of the memory word. Any block can go into any line of the cache. This means that the word id bits are used to identify which word in the block is needed, but the tag becomes all of the remaining bits. This enables the placement of any word at any place in the cache memory. It is considered to be the fastest and most flexible mapping form. In associative mapping, the index bits are zero.
Associative Mapping – Structure
3. Set-Associative Mapping
This form of mapping is an enhanced form of direct mapping where the drawbacks of direct mapping are removed. Set associative addresses the problem of possible thrashing in the direct mapping method. It does this by saying that instead of having exactly one line that a block can map to in the cache, we will group a few lines together creating a set. Then a block in memory can map to any one of the lines of a specific set. Set-associative mapping allows each word that is present in the cache can have two or more words in the main memory for the same index address. Set associative cache mapping combines the best of direct and associative cache mapping techniques. In set associative mapping the index bits are given by the set offset bits. In this case, the cache consists of a number of sets, each of which consists of a number of lines.

Set-Associative Mapping
Relationships in the Set-Associative Mapping can be defined as:
m = v * k
i= j mod vwhere
i = cache set number
j = main memory block number
v = number of sets
m = number of lines in the cache number of sets
k = number of lines in each set

Set-Associative Mapping – Structure
For more, you can refer to the Difference between Types of Cache Mapping.
Application of Cache Memory
Here are some of the applications of Cache Memory.
- Primary Cache: A primary cache is always located on the processor chip. This cache is small and its access time is comparable to that of processor registers.
- Secondary Cache: Secondary cache is placed between the primary cache and the rest of the memory. It is referred to as the level 2 (L2) cache. Often, the Level 2 cache is also housed on the processor chip.
- Spatial Locality of Reference: Spatial Locality of Reference says that there is a chance that the element will be present in close proximity to the reference point and next time if again searched then more close proximity to the point of reference.
- Temporal Locality of Reference: Temporal Locality of Reference uses the Least recently used algorithm will be used. Whenever there is page fault occurs within a word will not only load the word in the main memory but the complete page fault will be loaded because the spatial locality of reference rule says that if you are referring to any word next word will be referred to in its register that’s why we load complete page table so the complete block will be loaded.
Advantages
- Cache Memory is faster in comparison to main memory and secondary memory.
- Programs stored by Cache Memory can be executed in less time.
- The data access time of Cache Memory is less than that of the main memory.
- Cache Memory stored data and instructions that are regularly used by the CPU, therefore it increases the performance of the CPU.
Disadvantages
- Cache Memory is costlier than primary memory and secondary memory.
- Data is stored on a temporary basis in Cache Memory.
- Whenever the system is turned off, data and instructions stored in cache memory get destroyed.
- The high cost of cache memory increases the price of the Computer System.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cache memory plays a crucial role in making computers faster and more efficient. By storing frequently accessed data close to the CPU, it reduces the time the CPU spends waiting for information. This means that tasks are completed quicker, and the overall performance of the computer is improved. Understanding cache memory helps us appreciate how computers manage to process information so swiftly, making our everyday digital experiences smoother and more responsive.
Frequently Asked Questions on Cache Memory – FAQs
Why is cache memory important?
Cache memory is important because it helps speed up the processing time of the CPU by providing quick access to frequently used data, improving the overall performance of the computer.
How does cache memory work?
Cache memory works by storing copies of frequently accessed data from the main memory. When the CPU needs data, it first checks the cache. If the data is found (a “cache hit”), it is quickly accessed. If not (a “cache miss”), the data is fetched from the slower main memory.
Can cache memory be upgraded?
Cache memory is built into the CPU or located very close to it, so it cannot be upgraded separately like RAM. To get more or faster cache, you would need to upgrade the entire CPU.
Is cache memory volatile?
Yes, cache memory is volatile, meaning it loses all stored data when the computer is turned off, just like RAM.